Automotive-SW-testing
Automotive SW testing?

the process of verifying and validating a vehicle’s software to ensure it functions correctly, safely, and reliably, especially for safety-critical systems like braking and steering. This includes various tests like functional, structural coverage, and worst-case execution time analysis, and is guided by industry standards such as ISO 26262 (for functional safety), MISRA (for coding standards), and AUTOSAR (for embedded software). Testing also increasingly includes cybersecurity testing due to the connected nature of modern cars.
Industry standards:
- ISO 26262: A standard for functional safety in road vehicles, guiding risk-based development of safety-critical software.
- MISRA C: Provides coding guidelines to improve the safety and security of C/C++ software used in automotive systems.
- AUTOSAR: Defines a standard architecture for the development of embedded software for electronic control units (ECUs).
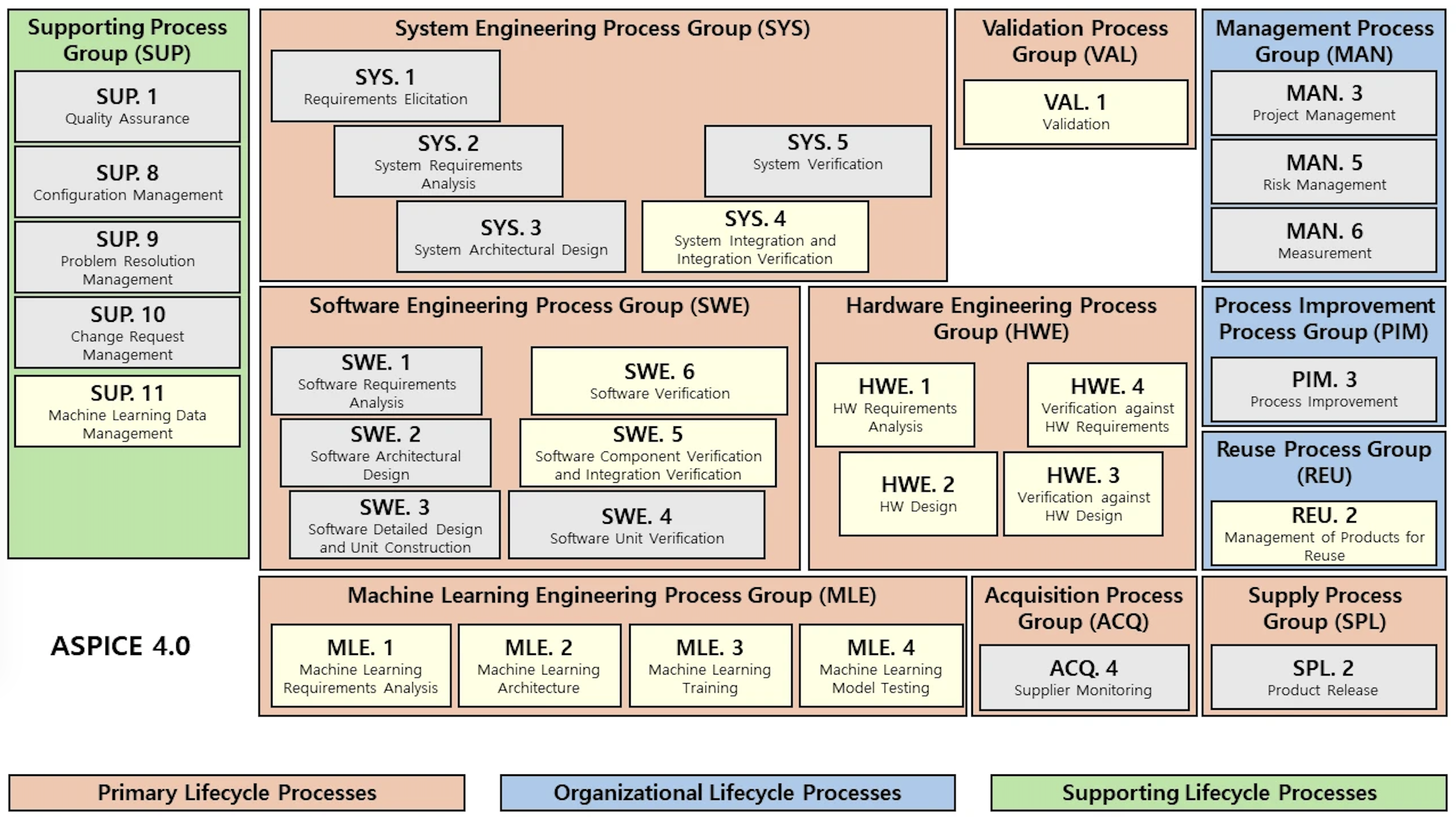
- ASPICE (automotive software process improvement capability determination): To improve the quality and sophistication of software and embedded systems development processes.
Testing levels
Tests are performed at different levels, including:
- Software Unit Verification
- Software Integration and Integration Test
- Software Qualification Test
- System Integration and Integration Test
- System Qualification Test
V&V (Verification & Validation)
Verification and validation (also abbreviated as V&V) are independent procedures that are used together for checking that a product, service, or system meets requirements and specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose.These are critical components of a quality management system such as ISO 9000. The words “verification” and “validation” are sometimes preceded with “independent”, indicating that the verification and validation is to be performed by a disinterested third party. “Independent verification and validation” can be abbreviated as “IV&V”.

TDD test
In the context of V&V (Verification and Validation), TDD (Test-Driven Development) primarily falls under the Verification stage TDD is based on writing automated unit tests. These tests constantly verify that each small unit of code behaves exactly as specified, ensuring the software is being built correctly at the lowest level.
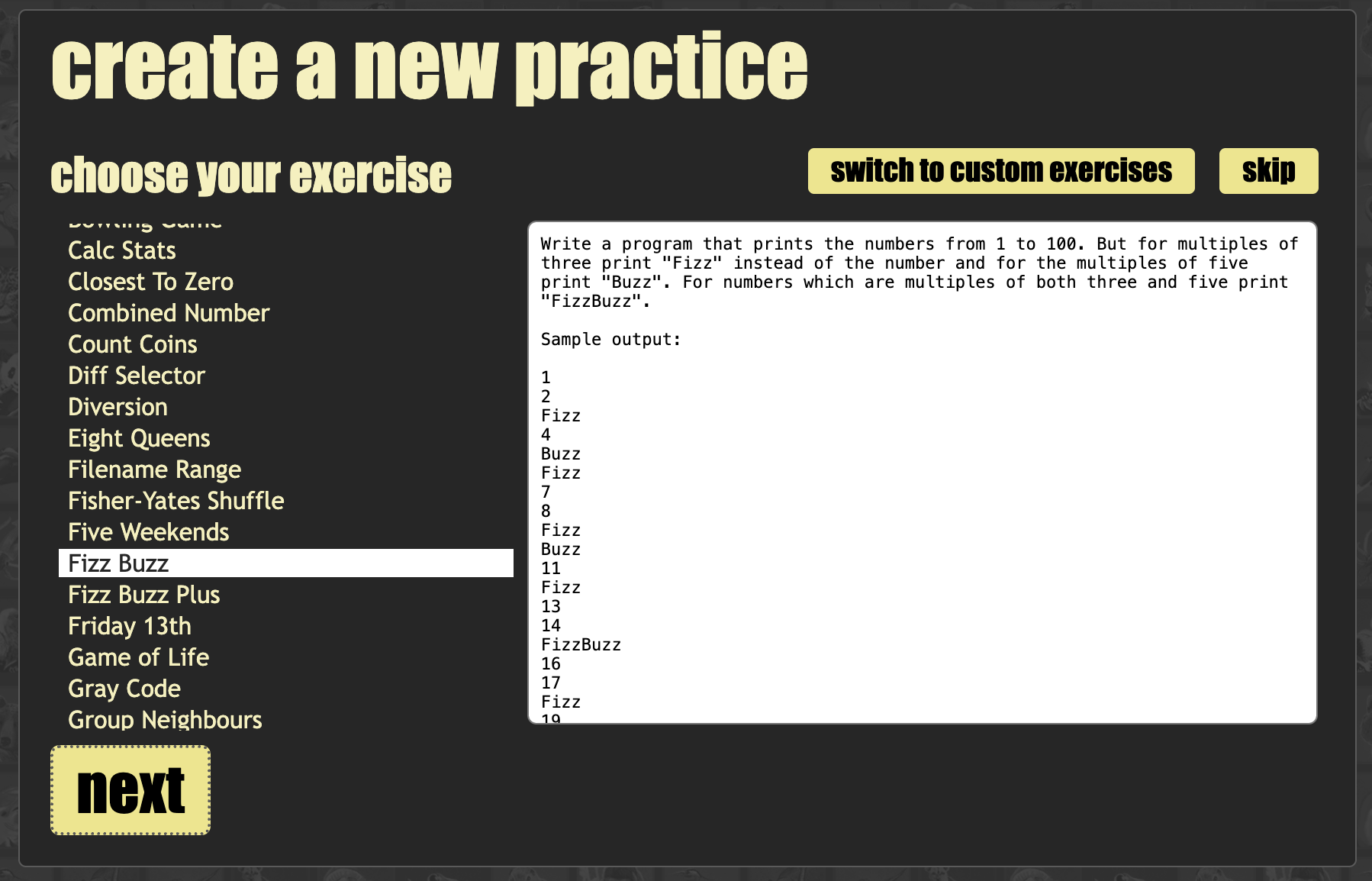
Try TDD test on cyber dojo

select your excercise, I choose Fizz Buzz
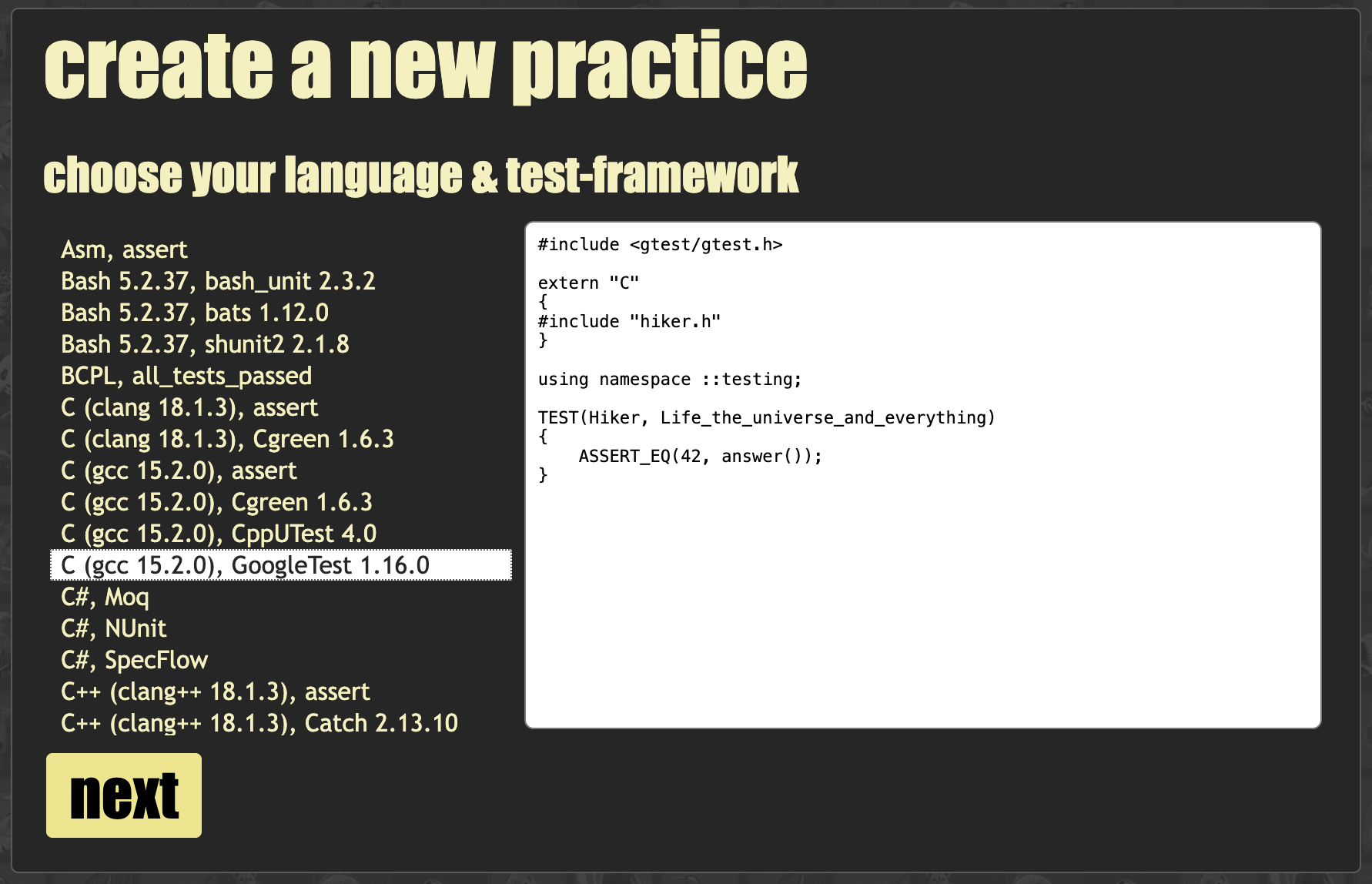
choose language and test-framework
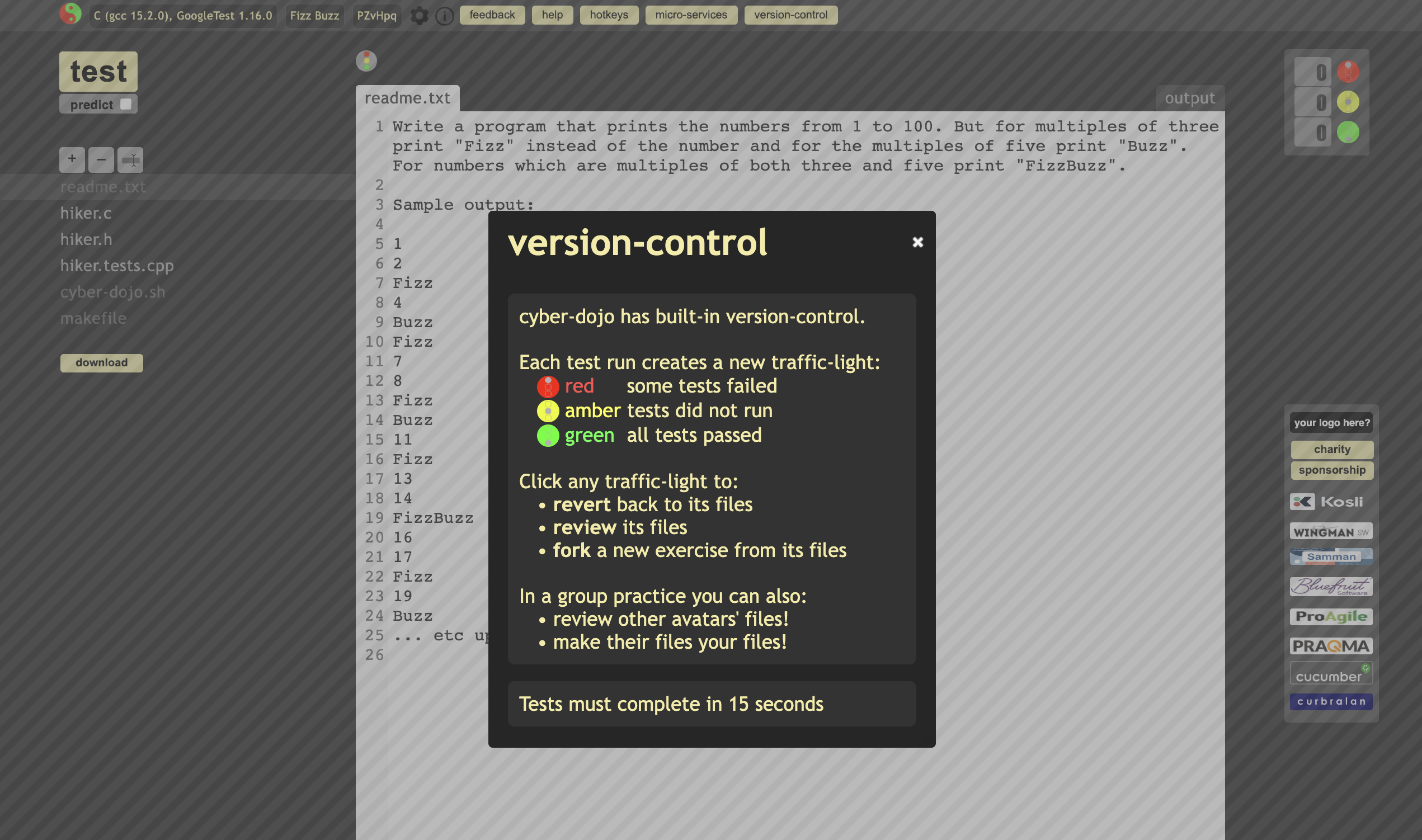
choose practice type, ensemble or classroom or solo. I select solo.

Then, automaticallty ID is generated. If you want to check my practice, you can use my ID PZvHpq and check it anytime.

add new TEST function
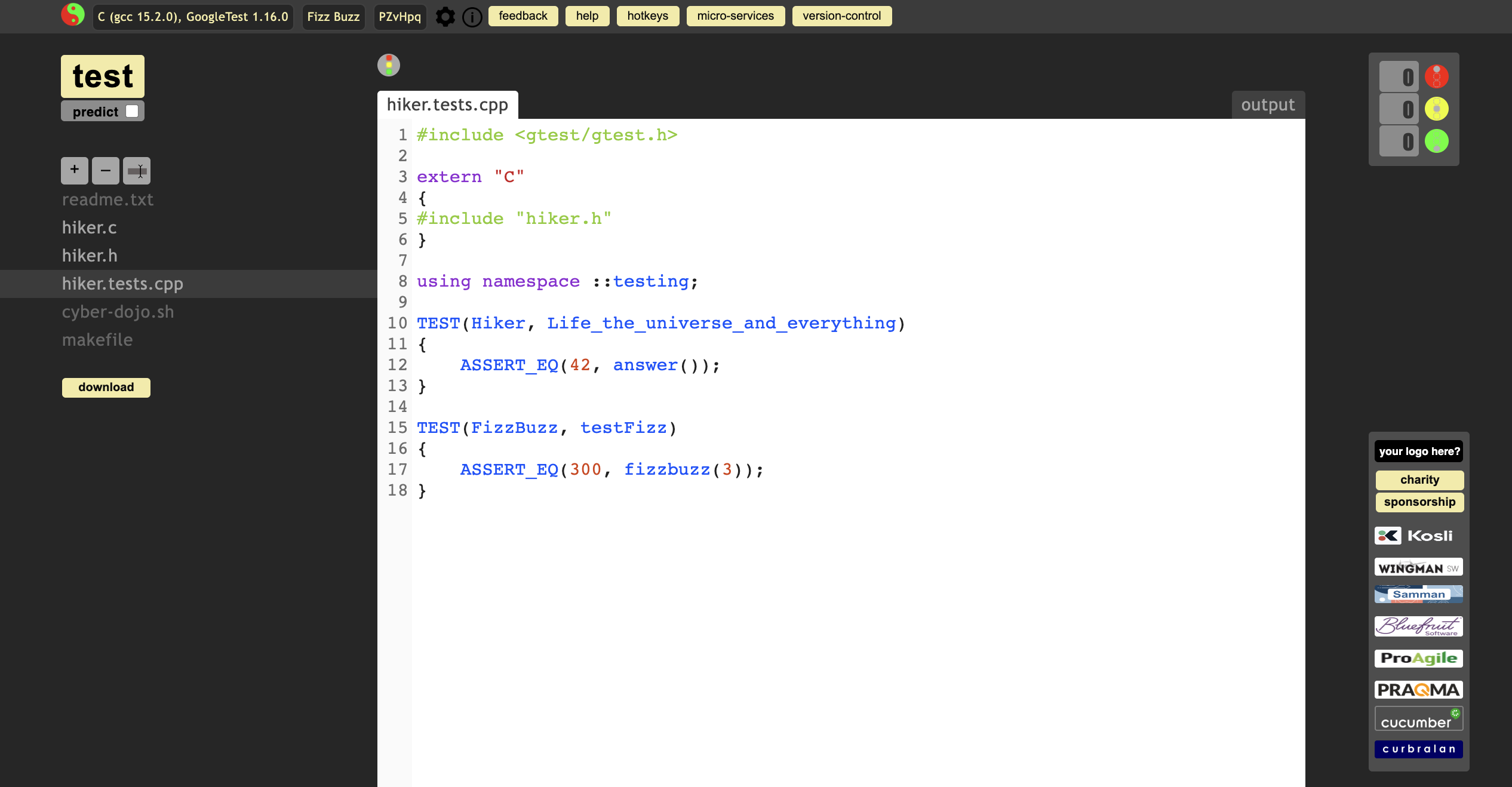
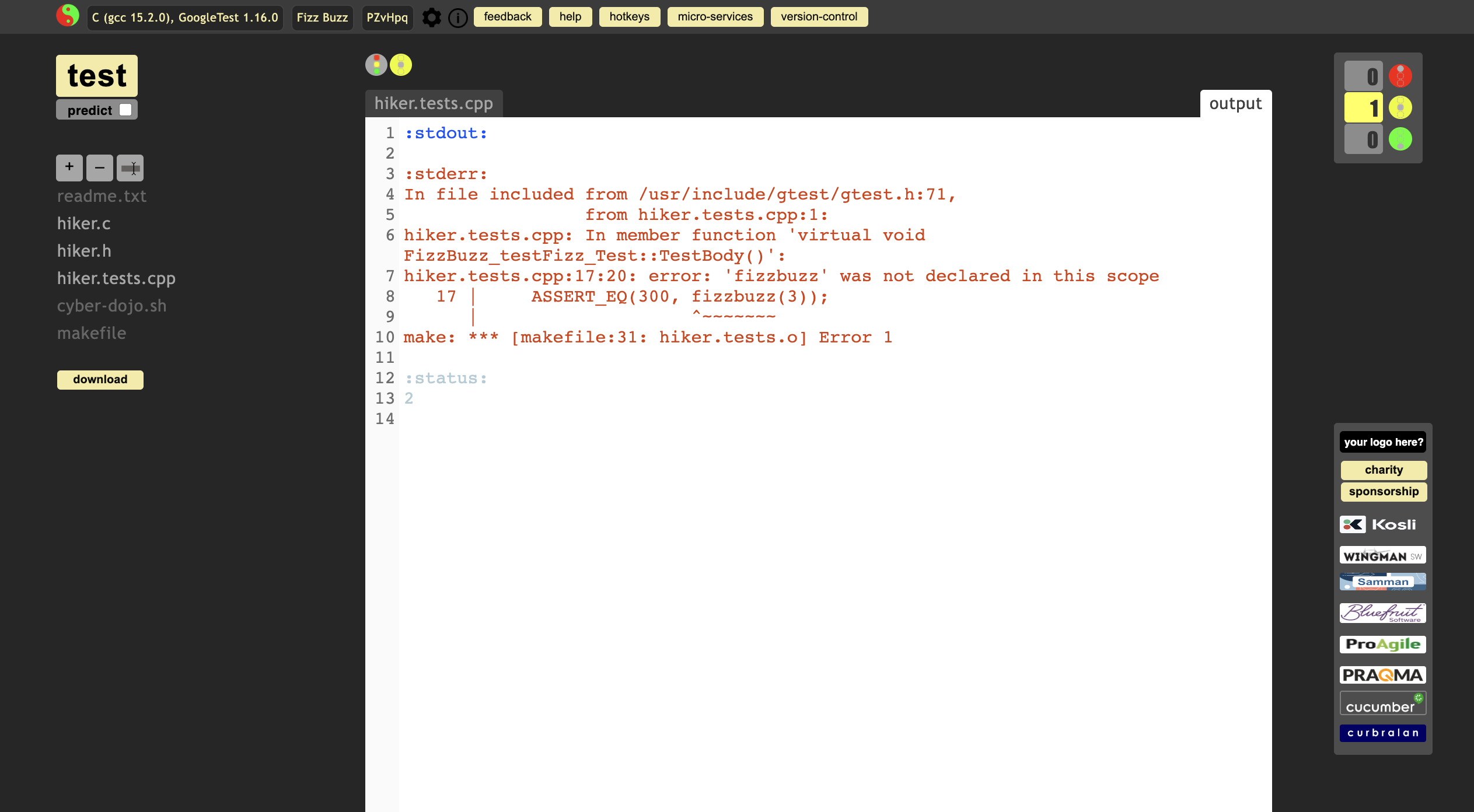
test it, but get the error msg
update hiker.c and hiker.h as below:
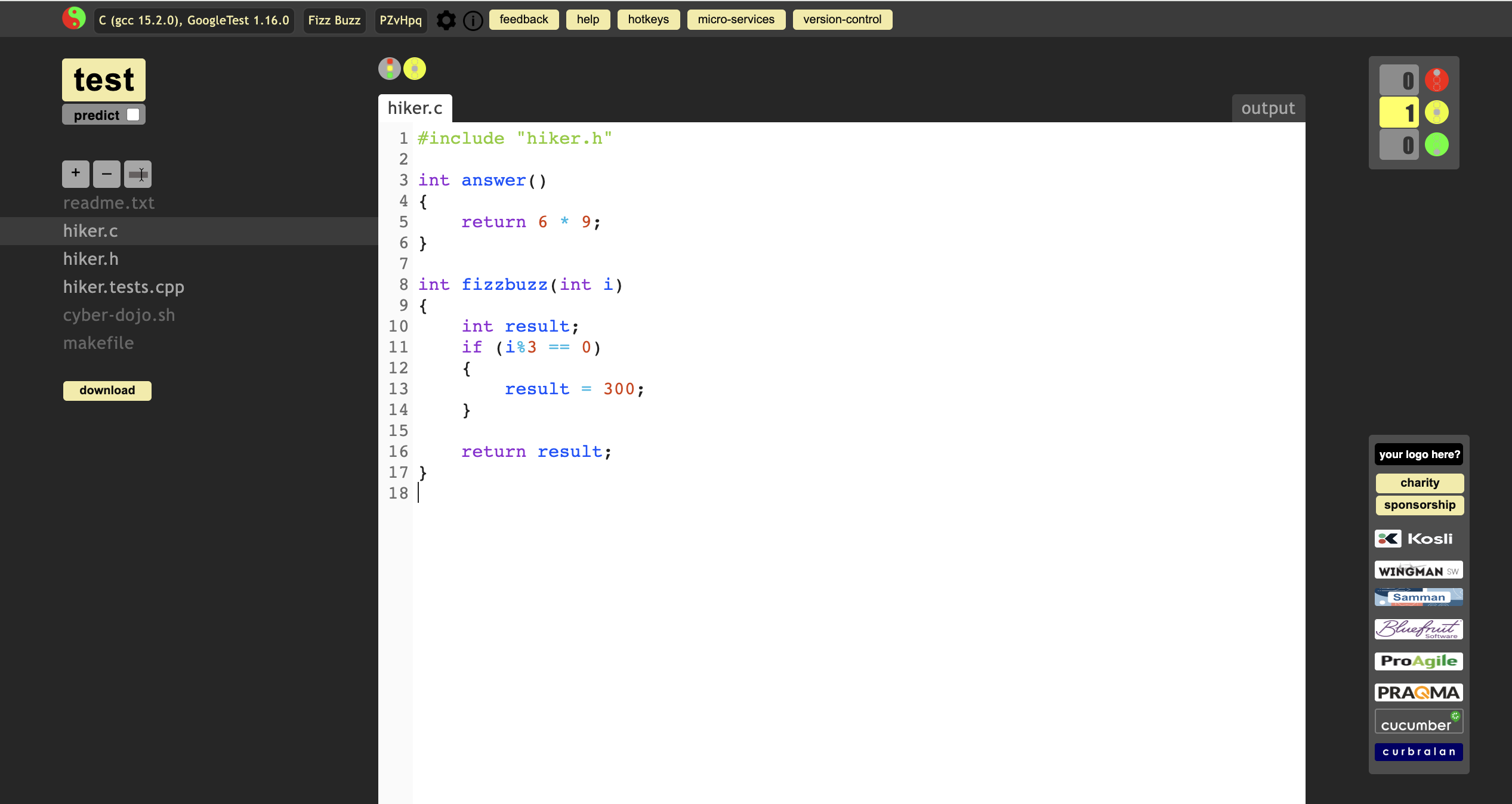
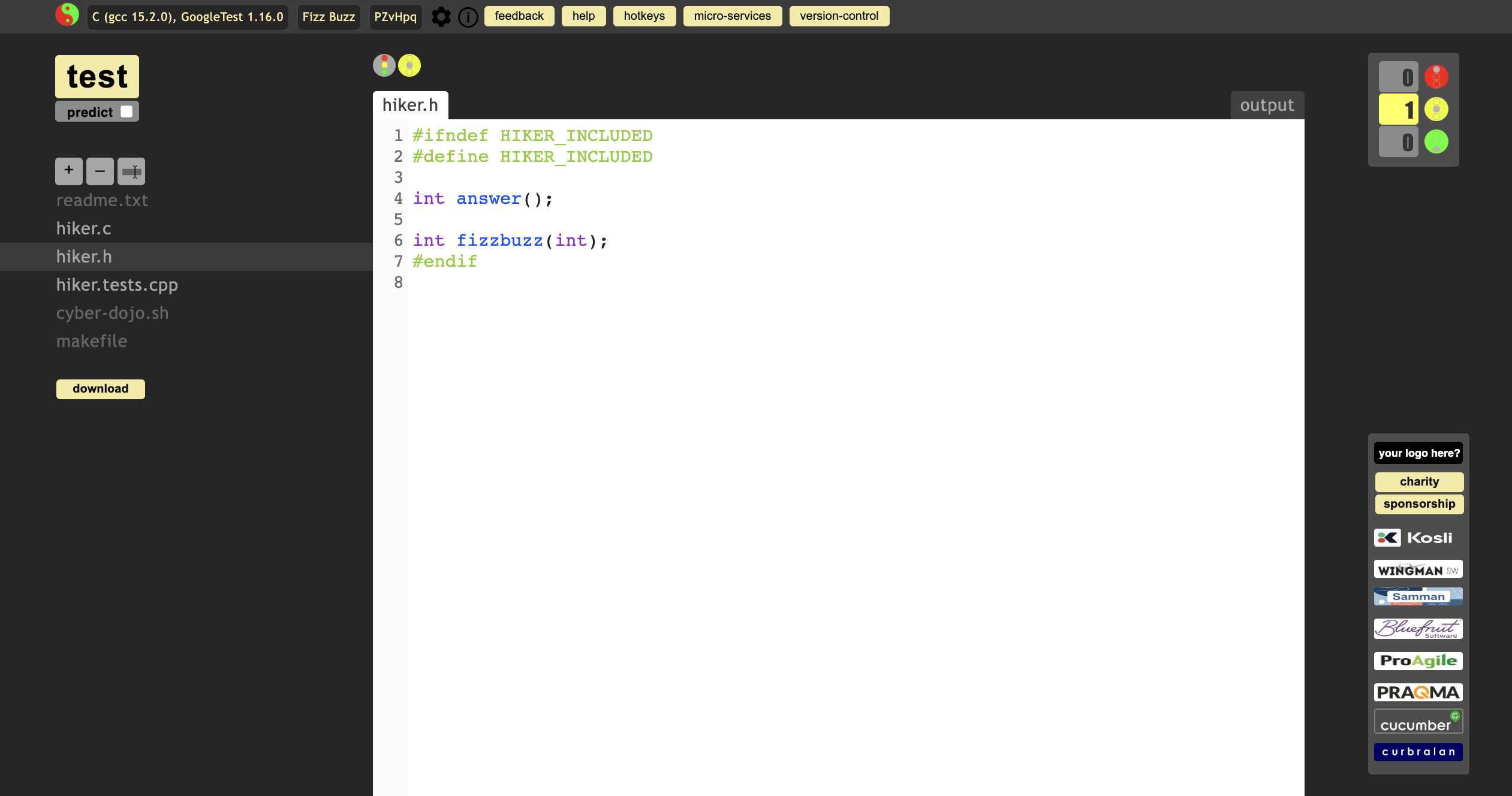
Test it again. But still get the error msg. why?
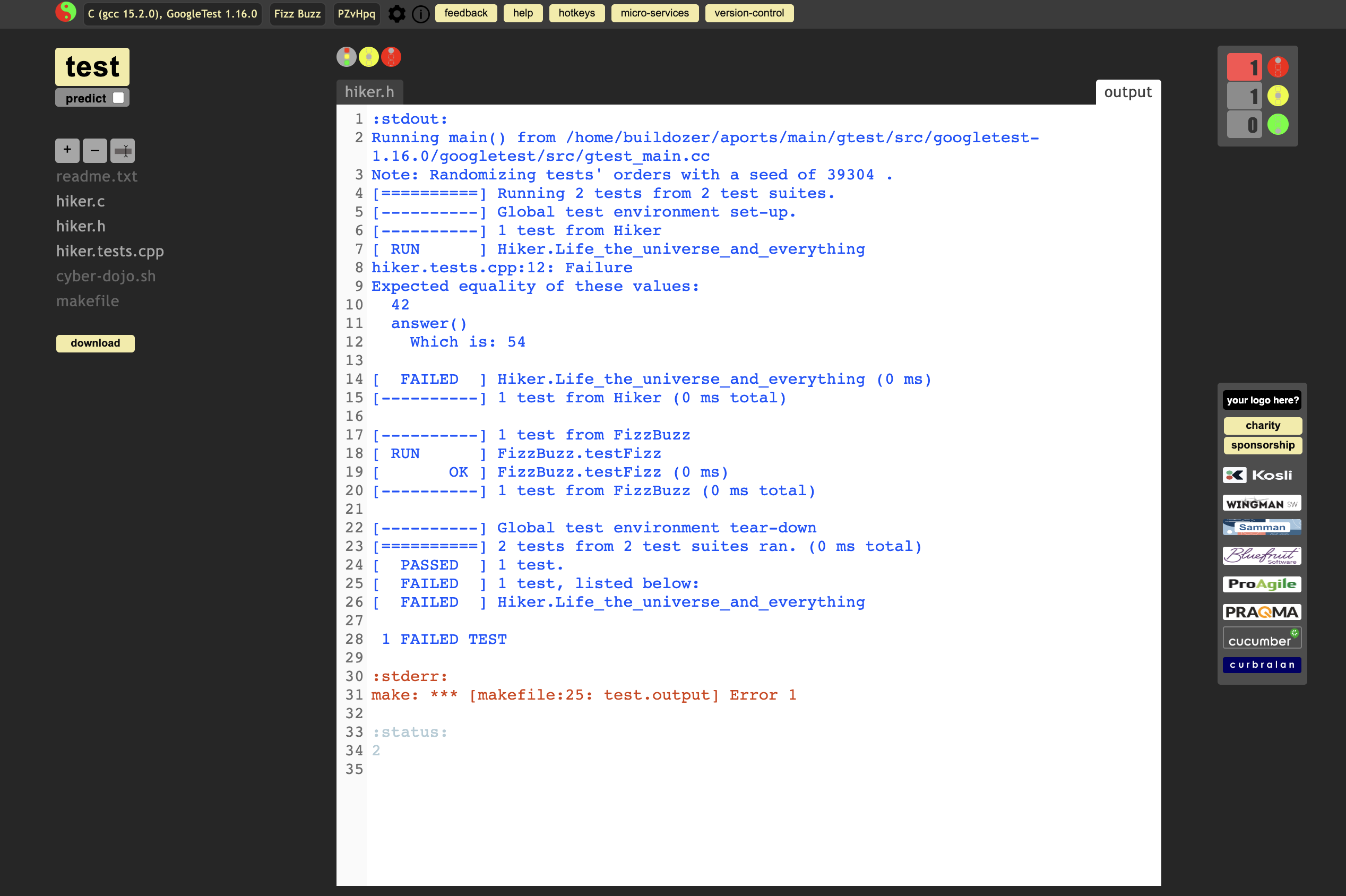
Thus, fix hiker.c.
previous version
int answer()
{
return 6 * 9
}
updated version
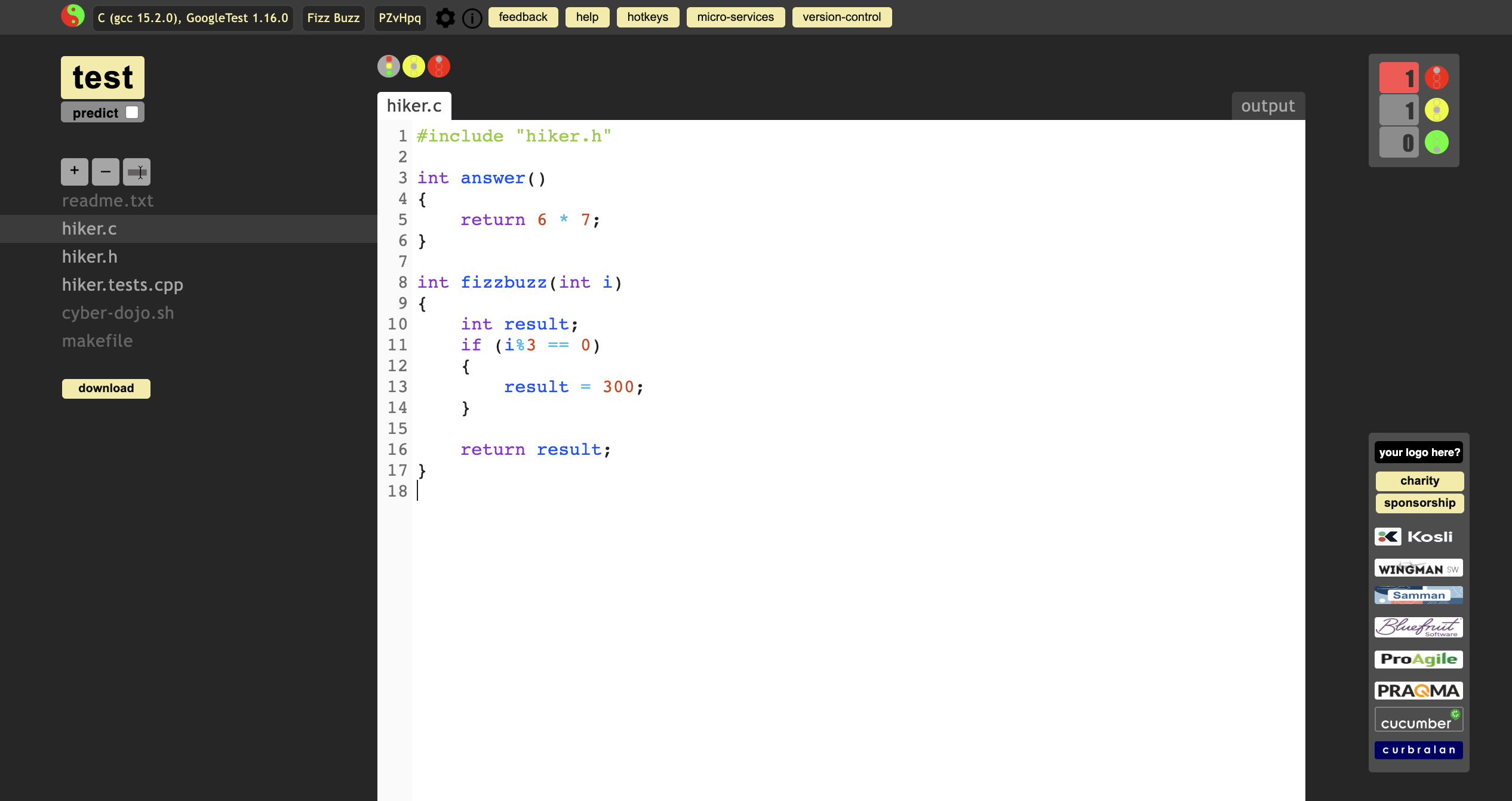
Test again and not work well.
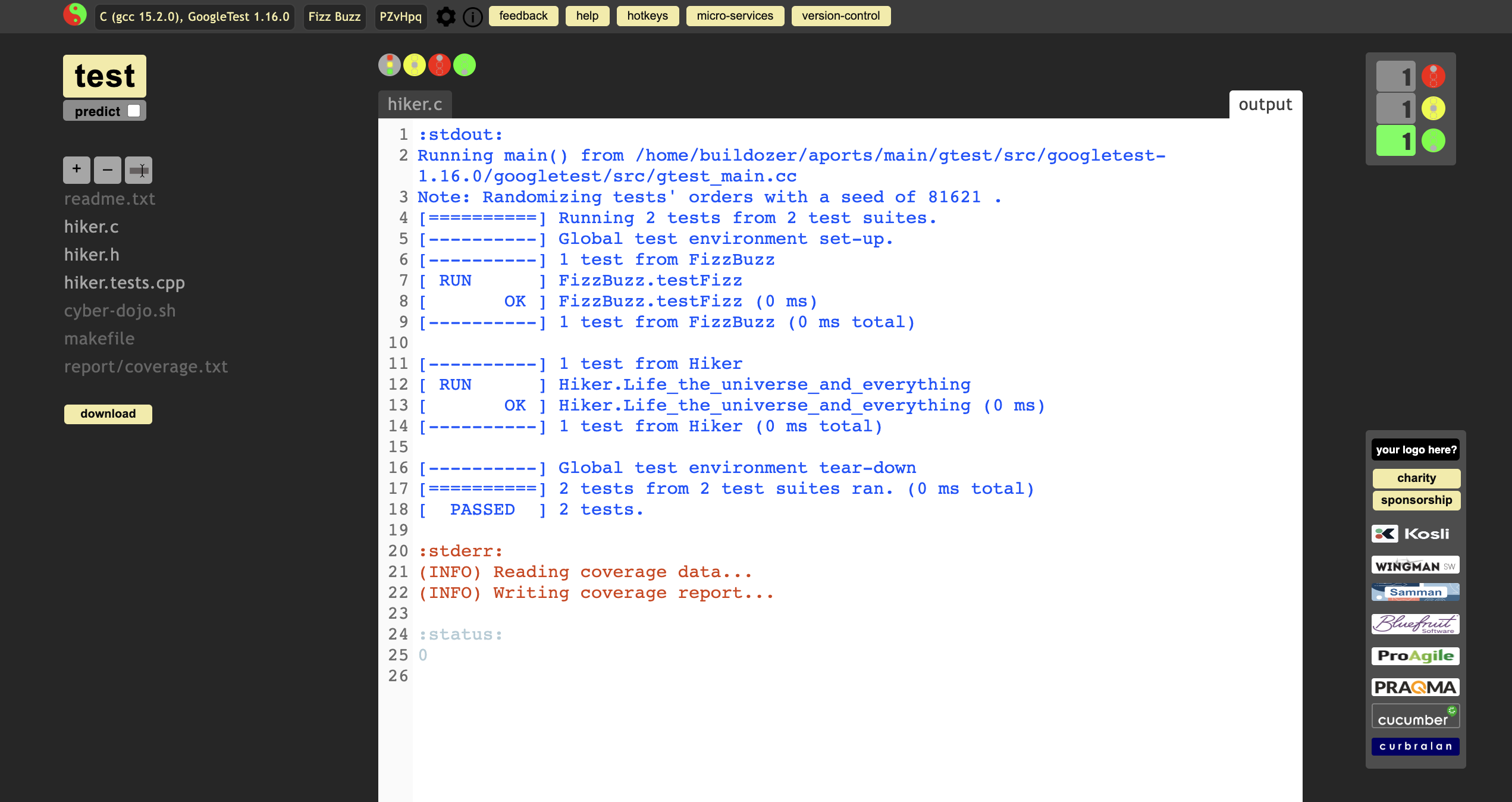
do refactoring as below:
- initialize result
- consider different variable name intputNumber instead of i
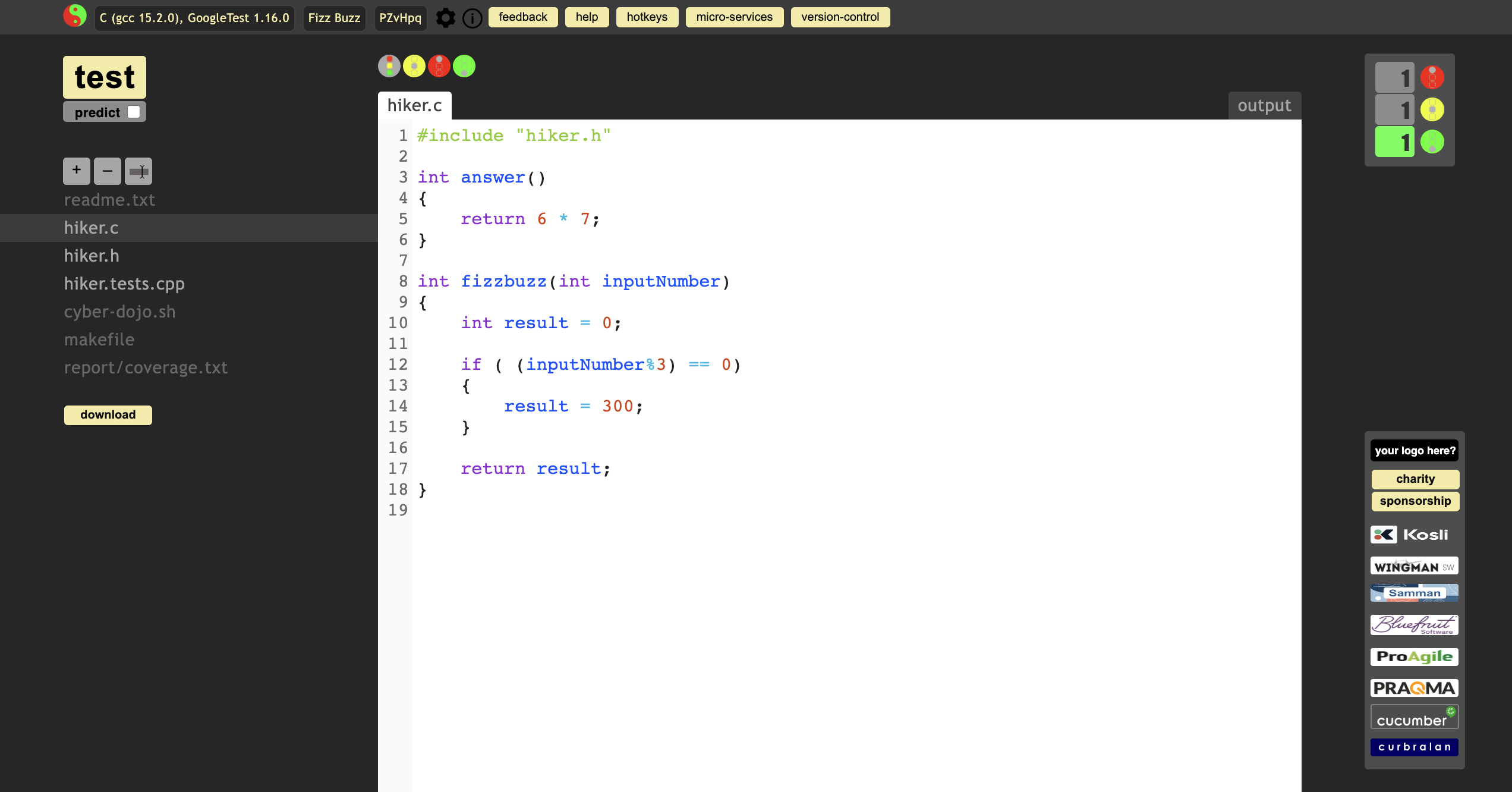
Test it again
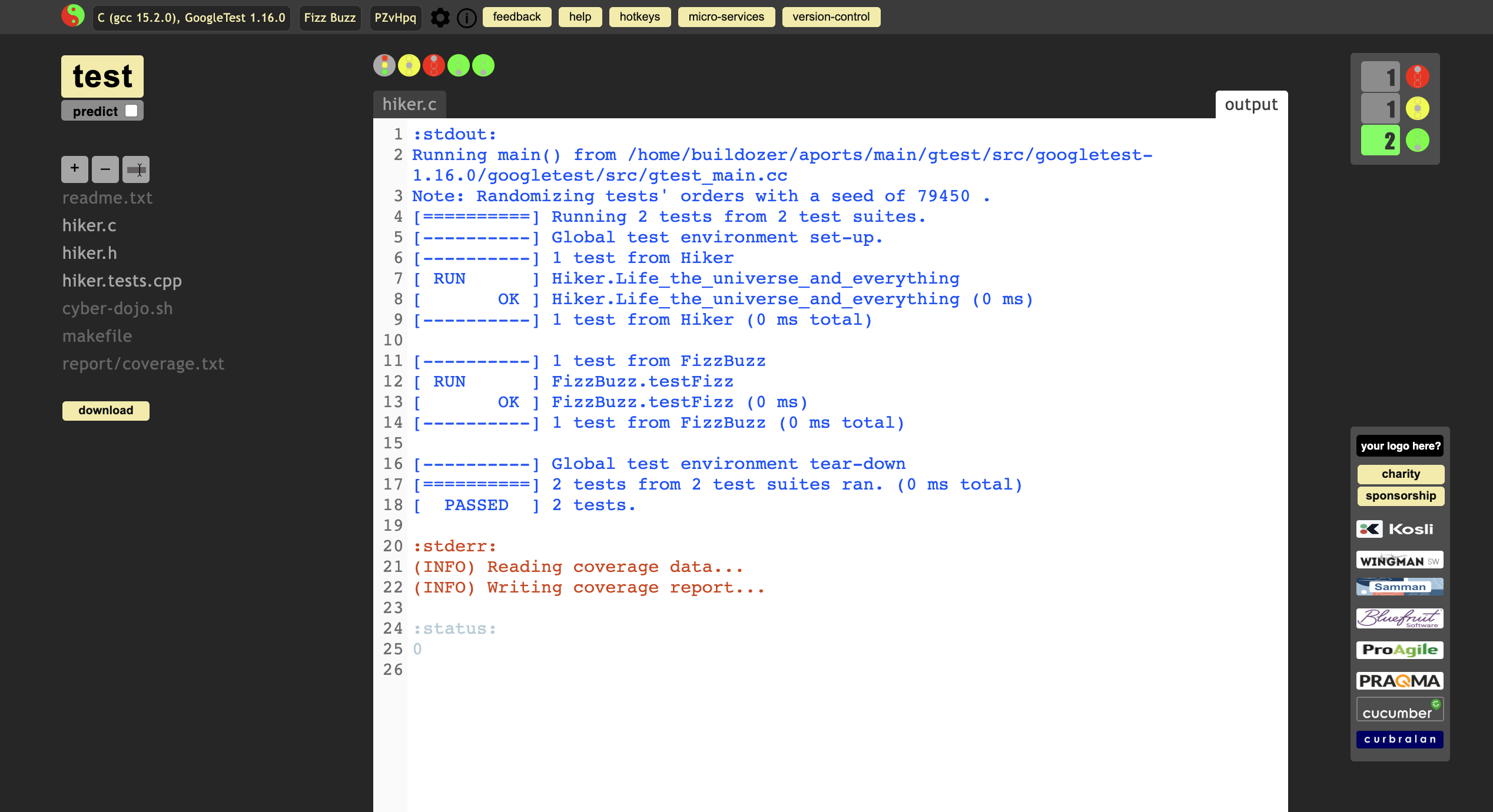
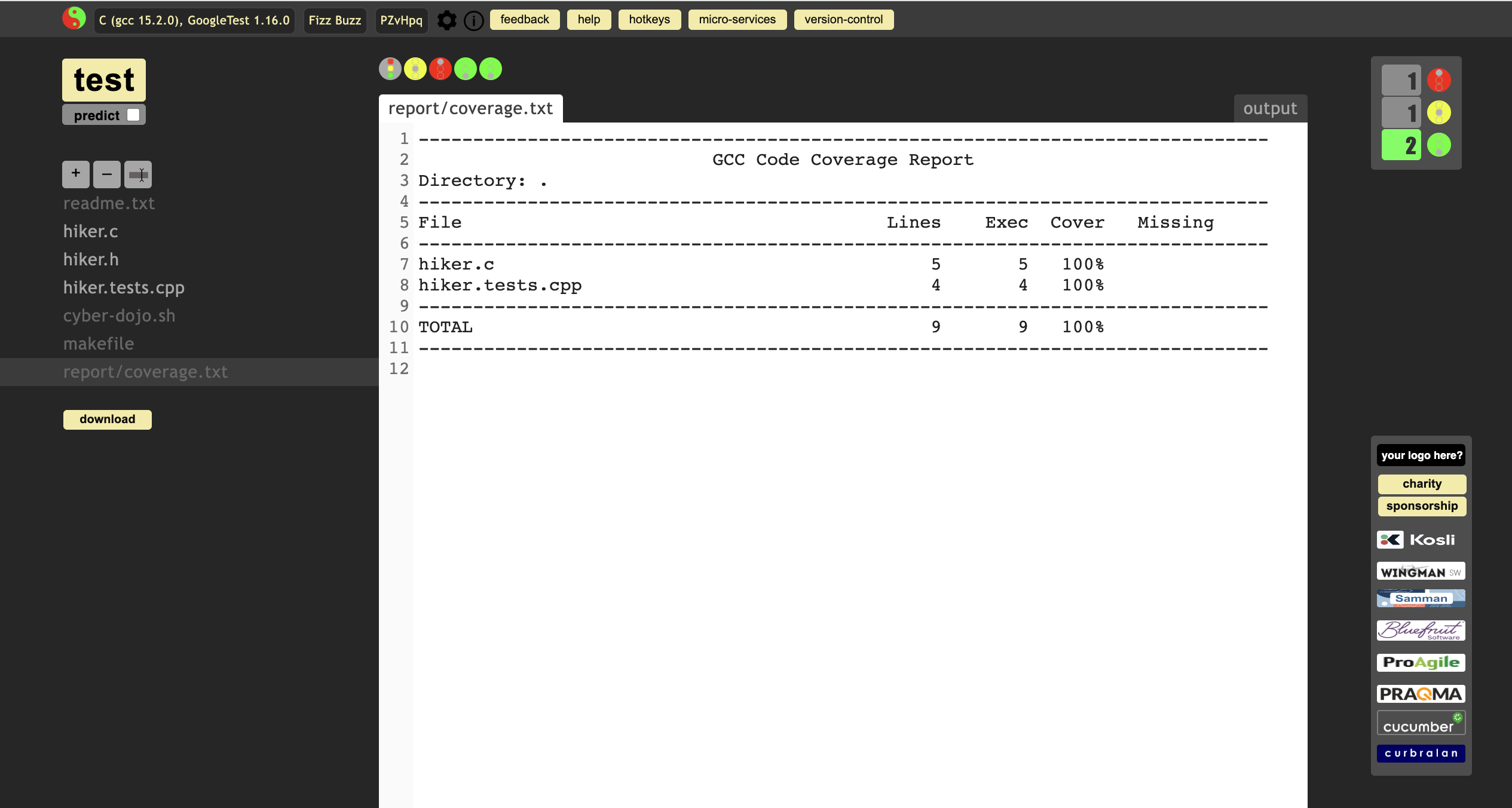
Finally, check the GCC code coverage Report which is automatically generated.
You can check it by yourself using the attached file, cyber-dojo-2025-10-25-PZvHpq.tgz
🦦 Thanks for reading. Hope to see you again!