Bayesian Optimization (BO)
Bayesian Optimization (베이지안 최적화) 란?
베이지안 최적화.
어디서부터 시작했는지는 모르겠지만, Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) 을 하다가 어느 순간부터 Bayesian의 세계로 빨려 들어가고 있는 것 같다.

요즘은 정말 아무 생각없이 의식의 흐름에 따라 공부하고 있는 것 같다.그래도 재밌는 것은 나름 흥미를 느끼고 있다.
도시에 처음 올라와 모든 것이 신기한 🐭 시골 쥐의 AI 도시 탐방기 같다.

본 글은 A tutorial on bayesian Optimization (2018) [1] 논문을 기반으로 이해하면서 필요한 내용들을 더해나가는 형식으로 작성하였다.
우선, Bayesian optimization에 대하여 wikipedia를 검색해보면 다음과 같다 [2].
Bayesian optimization is a sequential design strategy for global optimization of black-box functions that does not assume any functional forms. It is usually employed to optimize expensive-to-evaluate functions.
뭔가 이해하기가 어려워, 좀 더 쉽게 풀이한 부분을 찾아보았다 [3].
Bayesian Optimization provides a principled technique based on Bayes Theorem to direct a search of a global optimization problem that is efficient and effective. It works by building a probabilistic model of the objective function, called the surrogate function, that is then searched efficiently with an acquisition function before candidate samples are chosen for evaluation on the real objective function.
정리하자면 베이지안 최적화란 목적함수 (objective function, f)를 최대화 혹은 최소화하는 최적해를 찾는 기법으로 베이지안 정리를 기반으로 하고 있다. 또한, 이는 objective function과 acquisition function이라는 두 개의 큰 요소로 구성되어 있다 [1].
BayesOpt consists of two main components : a Bayesian statistical model for modeling the objective function, and an acquisition function for deciding where to sample next.
그런데, 여기서 확인하고 가야 할 부분이 있다. 일부 글에서는 베이지안의 최적화는 surrogate model과 acquisition function로 구성되어 있다고도 하는데, 사실 둘 다 맞는 말이라고 생각한다. surrogate model이란 literally 대리(대용) 모델 로 목적함수인 objective function을 추정하는 ML모델로, Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) 을 사용하고 있다. 따라서 objective function + surrogate model + acquisition function 이 삼총사가 베이지안 최적화의 주요 구성 요소들이라고 기억하면 좋을 것 같다.
이외에 베이지안 최적화에 대하여 좀 더 자세한 내용을 이해하기에 앞서 몇가지 키워드를 기억하고 가면 좋을 것 같다.
◦ Global optimization
◦ Objective function
◦ Surrogate model
◦ Acquisition function
◦ Gaussian Process Regression (GPR)
◦ Black-box function
◦ Bayesian Theore
☾ Table of contents
☺︎ Optimization?
- Global optimization vs Local optimization
- Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO)
☺︎ Bayesian Optimization (in short, BO or BayesOpt)
- Objective function, f
- Surrogate model
- Acquisition model
☺︎ Beauty of the Bayesian Optimization
☻ Reference
☺︎ Optimization
베이지안 최적화를 찾아보면, 심심치않게 global optimization과 hyperparameter optimization (HPO)이라는 말을 맞닥뜨리게 된다. 뭐지?
first things first으로, 중복되어 있는 단어인 optimization부터 확인해보자.
최적화 (optimization)는 무엇일까? wikipedia의 설명은 다음과 같다 [4,5]
최적화(最適化, 영어: mathematical optimization 또는 mathematical programming)는 특정의 집합 위에서 정의된 실수값, 함수, 정수에 대해 그 값이 최대나 최소가 되는 상태를 해석하는 문제이다. 수리 계획 또는 수리 계획 문제라고도 한다. 물리학이나 컴퓨터에서의 최적화 문제는 생각하고 있는 함수를 모델로 한 시스템의 에너지를 나타낸 것으로 여김으로써 에너지 최소화 문제라고도 부른다.
수학적 관점에서의 최적화는
In mathematics, computer science and economics, an optimization problem is the problem of finding the best solution from all feasible solutions.
즉, 최적화라는 것은 가장 적절한 값 (혹은 someth)을 구하는 것이다. 여기서 의미하는 적절한 값이란 the best solutoin 구하라는 의미이다. Best solution? 이게 무슨 말이지? 사실 이런 정확하지 못한 표현은 굉장히 불편하다. 즉, 이해가 잘 안되서 마음이 편치않다.
조금 다른 얘기지만, 아시는 분께서 갑자기 ML/DL이 편하냐고 물어보셨다. 편하는 것이 무슨 의미인지 여쭤보니, 그 분이 미국에서 공부하셨을때 담당 교수님께서 항상 “Do you feel comfortable?” 라고 물어보셨다한다. 맞다! 그런 맥락으로 생각 할 수 있다. 사실 이해하지 못하면 마음이 굉장히 불편하다. 논문을 읽다가 이해가 안되는데 뒷장을 넘길때는 뭔가 찝찝하고 답답하고 불편한 감정이 생긴다 (부르르르르~). 앗! 나만 그럴수도 있다 🤔

Anyhow, 그래서 최적화가 무엇이란 말인가?
사실, 위에서 설명한 최적화에 대한 definition은 너무 general해서 크게 와닿지 않는다. 따라서 우리가 관심있는 ML과 연관지어 생각해보면, 모델이 데이터를 잘 설명할수 있도록 모델 변수들에 관한 목적 함수를 최적화한다 에서 최적화의 의미를 이해할수 있다. 여기서 변수들을 매개변수라 생각한다면 Hyperparamter optimization (HPO) 이라고 볼수 있을 것 같다.
Many algorithms in machine learning optimize an objective function with respect to a set of desired model parameters that control how well a model explains the data: Finding good parameters can be phrased as an optimization problem. Examples include: (i) linear regression, where we look at curve-fitting problems and optimize linear weight parameters to maximize the likelihood; (ii) neural-network auto-encoders for dimensionality reduction and data compression, where the parameters are the weights and biases of each layer, and where we minimize a reconstruction error by repeated application of the chain rule; and (iii) Gaussian mixture models for modeling data distributions, where we optimize the location and shape parameters of each mixture component to maximize the likelihood of the model [6].
HPO에 대한 설명은 아래서 좀 더 자세히 다루도록 하자.
☻ Global optimization vs Local optimization
위에서 Bayesian optimizaiton에 대해서 Bayesian optimization is a sequential design strategy for global optimization of black-box functions [2] 이라 했는데, 여기서 Global optimization이라는 것이 무엇인지 알아보고자 한다. 나아가 Global 과 Local 최적화 사이의 차이도 확인하고자 한다.
우선, Global optimization이란,
Global optimization is a branch of applied mathematics and numerical analysis that attempts to find the global minima or maxima of a function or a set of functions on a given set [7]
Global optimization이란 최적화에서 찾고자 하는 가장 적절한 최대 혹은 최소 를 찾는데, global 값을 찾아가는 것이다. Global이 있다면 당연히 Local도 있을테니, Local optimization과 비교해서 확인해보면
Local optimization involves finding the optimal solution for a specific region of the search space, or the global optima for problems with no local optima. Global optimization involves finding the optimal solution on problems that contain local optima. How and when to use local and global search algorithms and how to use both methods in concert [8].
자, Global 과 Local 의 사전적 의미부터 확인하면 다음과 같다 [9].
◦ Global
1. 세계적인
2. 전반[전체/포괄]적인
◦ Local
1. 지역의, 현지의
2. 일부의
간단한 schematic으로 확인하면 아래와 같다 (아래 schematic은 제가 작성한 것 입니다.).
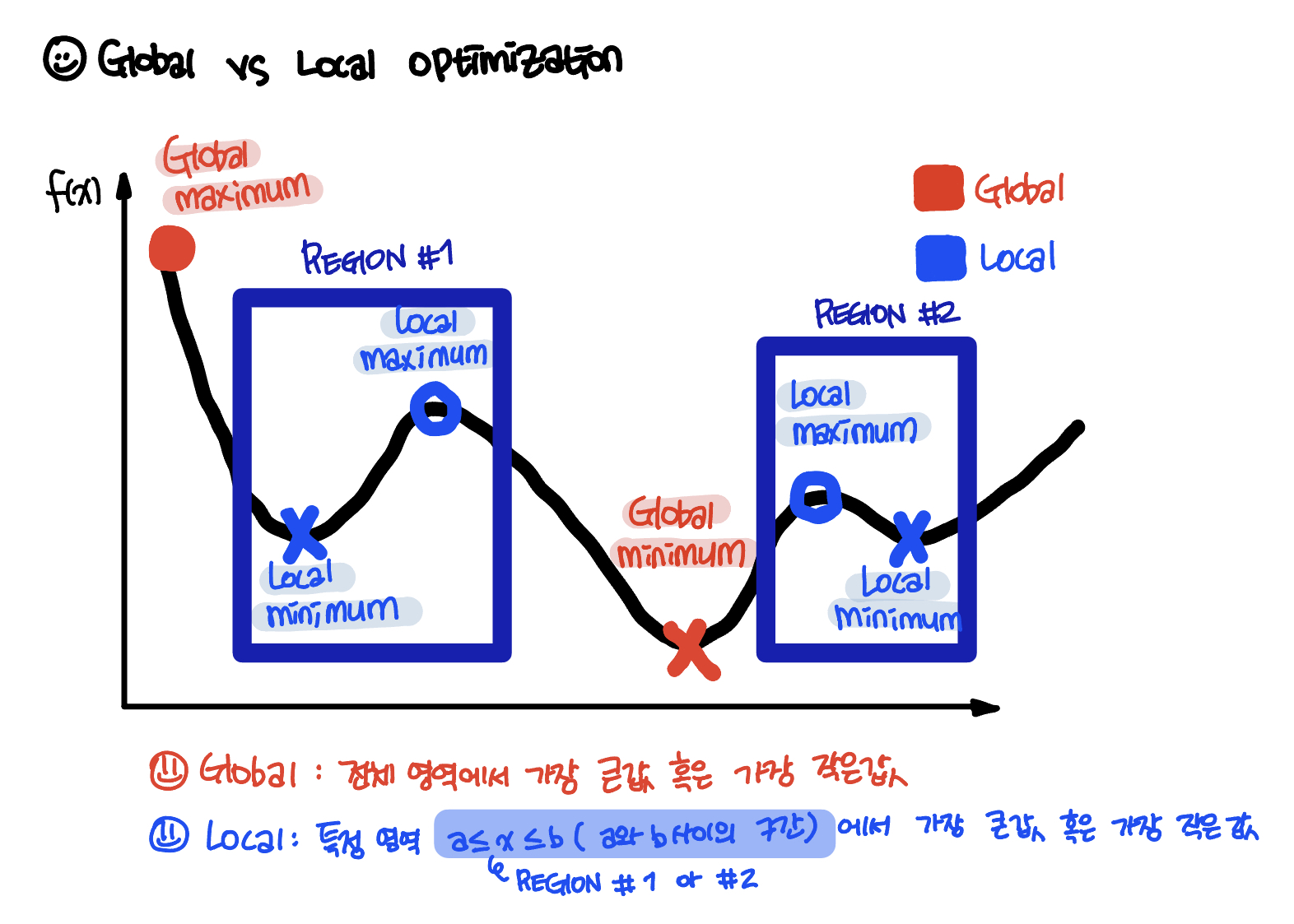
전반적인 혹은 전체적인 함수나 값들에서 최적화된 혹은 적절한 혹은 best 최대 혹은 최소를 찾는지 (Global optimization) 아니면 지역에서 혹은 일부의 함수나 값들에서 최적화된 혹은 적절한 혹은 best 최대 혹은 최소를 찾는지 (Local optimization)에 따라 나눠진다고 볼 수 있다. 따라서 이러한 Global minimum 혹은 Global maximum을 찾는 것은 굉장히 복잡한 일이다. 그리고 잘못하다가 Local minimum이나 Local maximum에 잡혀버릴 가능성도 있기 때문이다.
우선은 이정도의 개념만 갖고 가보도록 하자.
☻ Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO)
ML/DL에서 사용되는 optimization은 대부분 학습을 수행하기 사전에 설정하는 hyperparameter(초매개변수)의 최적값 탐색하는 문제 에 사용된다.
우선, Hyperparameter에 대해 알아보자면, 이는 learning 시작하기 전에 미리 정하는 값이다. 모델로 learning하는 값이 아니라 training전 사전에 설정해서 주어지는 값으로 최적의 모델을 구하기 위해서 tuning을 해줄 필요가 있다. 따라서, Hyperparamter tuning이라는 하는 것이다.
Hyperparameters refer to the parameters that the model cannot learn and need to be provided before training. Hyperparameter tuning basically refers to tweaking the parameters of the model, which is basically a lengthy process [10].
여기서, 좀 더 deep dive하게 들어가서 paramter앞에 Hyper-라는 말을 붙은 이유에 대해서 좀 더 자세히 살펴보자면,
Hyperparameters are parameters whose values control the learning process and determine the values of model parameters that a learning algorithm ends up learning. The prefix ‘hyper_’ suggests that they are ‘top-level’ parameters that control the learning process and the model parameters that result from it. As a machine learning engineer designing a model, you choose and set hyperparameter values that your learning algorithm will use before the training of the model even begins. In this light, hyperparameters are said to be external to the model because the model cannot change its values during learning/training [11].
hyperparameters that the learning algorithm will use to learn the optimal parameters that correctly map the input features (independent variables) to the labels or targets (dependent variable) such that you achieve some form of intelligence[11].
즉, learning proecss와 모델의 변수들을 제어하는 top-level의 변수라서 parameter앞에 Hyper-가 붙는 것이다. Hyper-의 사전적 의미를 확인하면 아래와 같고, top-level이라는 말과 상통한다 [12].
◦ hyper
1. above, beyond, SUPER-
2. excessively, excessive
따라서 최적의 hyperparamter를 제공해주는 것이 최적의 model을 구현하는데 중요하다고 볼 수 있다.
이러한 HPO에는 여러가지 방법이 있다 [10].
◦ Manual search grid
◦ Grid search
◦ Random search (Randomized Search)
◦ HyperOpt-Sklearn
◦ Bayesian optimiation
◦ Evolution algorithm
각각의 방법들에 대한 설명은 out of our scope이라서 더 이상 다루지 않고, 바로 Bayesian optimization으로 넘어가도록 한다.
☺︎ Bayesian Optimization
앞에서 언급된 부분을 통해 우리는 Optimization, 그 중 Global optimization까지 이해 할 수 있다. 그런데, 왜 Bayesian optimization 일까?
처음으로 돌아가서 Bayesian Optimization provides a principled technique based on Bayes Theorem to direct a search of a global optimization problem … It works by building a probabilistic model of the objective function, called the surrogate function, that is then searched efficiently with an acquisition function before candidate samples are chosen for evaluation on the real objective function. [1] 문구를 다시 한번 보면 살짝 힌트를 얻을 수 있다.
이제 우리가 집중해서 봐야 하는 부분은 Bayes Theorem, probabilistic model of the objective function, surrogate function, and acquisition function 이다. 말그대로 Bayes Theorem을 기반으로 하고 있어서 Bayesian Optimization이라는 것인데, 여기서 우리가 주목 할 부분은 과연 어떤식으로 Bayes Theorem 이 녹아져있는지 일 것 이다.
우선, 처음에 언급했던 베이지안 최적화의 삼총사인 objective function + surrogate model + acquisition function 기억해보길 바란다.이 아이들을 데리고 어떤식으로 최적화가 진행되는지에 대해서는 확인하면 다음과 같다 [13].
Since the objective function is unknown, the Bayesian strategy is to treat it as a random function and place a prior over it. The prior captures beliefs about the behavior of the function. After gathering the function evaluations, which are treated as data, the prior is updated to form the posterior distribution over the objective function. The posterior distribution, in turn, is used to construct an acquisition function (often also referred to as infill sampling criteria) that determines the next query point.
위의 문구를 집중해서 보니 prior, belief, posterior등 Bayes Theorem을 설명할때 나오는 반가운 얼굴들이 보인다. 아! 이래서 just Optimization이 아닌 Bayesian Optimization이구나 싶다. 그럼 우선 과정부터 좀 더 차근차근 확인하기 위해서 Pseudo-code로 본다면 아래와 같다 (아래 Pseudo-code는 논문 [14]에서 갖고와서 인용하였습니다.).
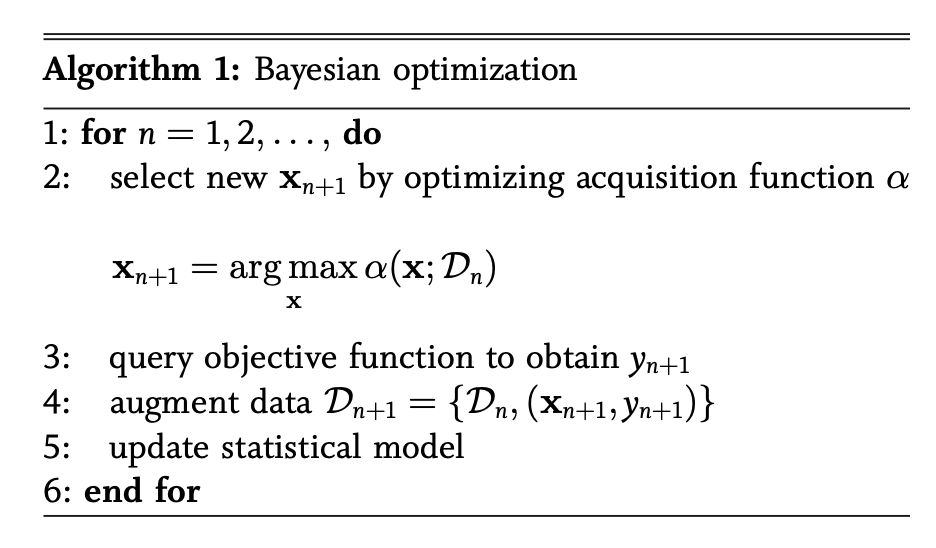
Fig. Pseudo-code of BO [14]
코드에서 5번인 statistical model은 surrogate model, 즉 GPR이라고 볼 수 있다. 프로세스는 surrogate model에서 GPR을 통해 Bayesian posterial probability distribution을 구하고 (mean, 𝝁과 variance, 𝝈^2), 그 값을 acquisition function에 적용해서 최대값을 갖는 next query p’t를 찾아냄에 따라 data augmentation을 하고 이 과정을 반복하면서 최적의 objective function, f 을 찾아가는 과정이 Bayesian Optimization이라고 할 수 있다.
이러한 과정을 schematic을 통해 좀 더 직관적으로 이해해보자(아래 Schematic of BO는 논문[14]의 Fig.1이며, BO의 설명을 위해서 갖고와서 인용하였습니다.).
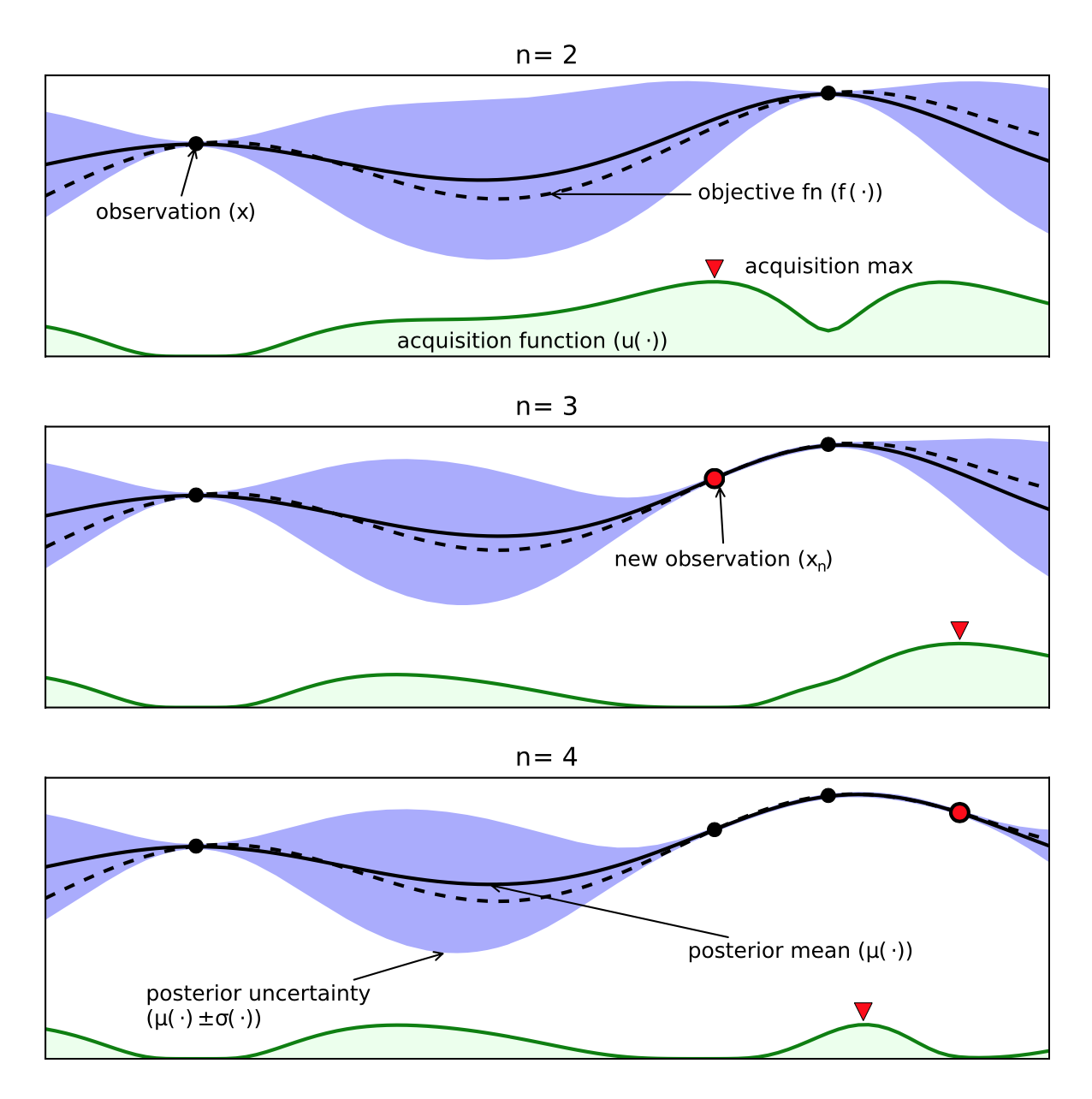
Fig. Schematic of BO [14]
이해를 돕기위해 설명을 추가하면 (아래 schematic은 위의 그림 일부에 내용을 추가해서 작성한 것 입니다.)
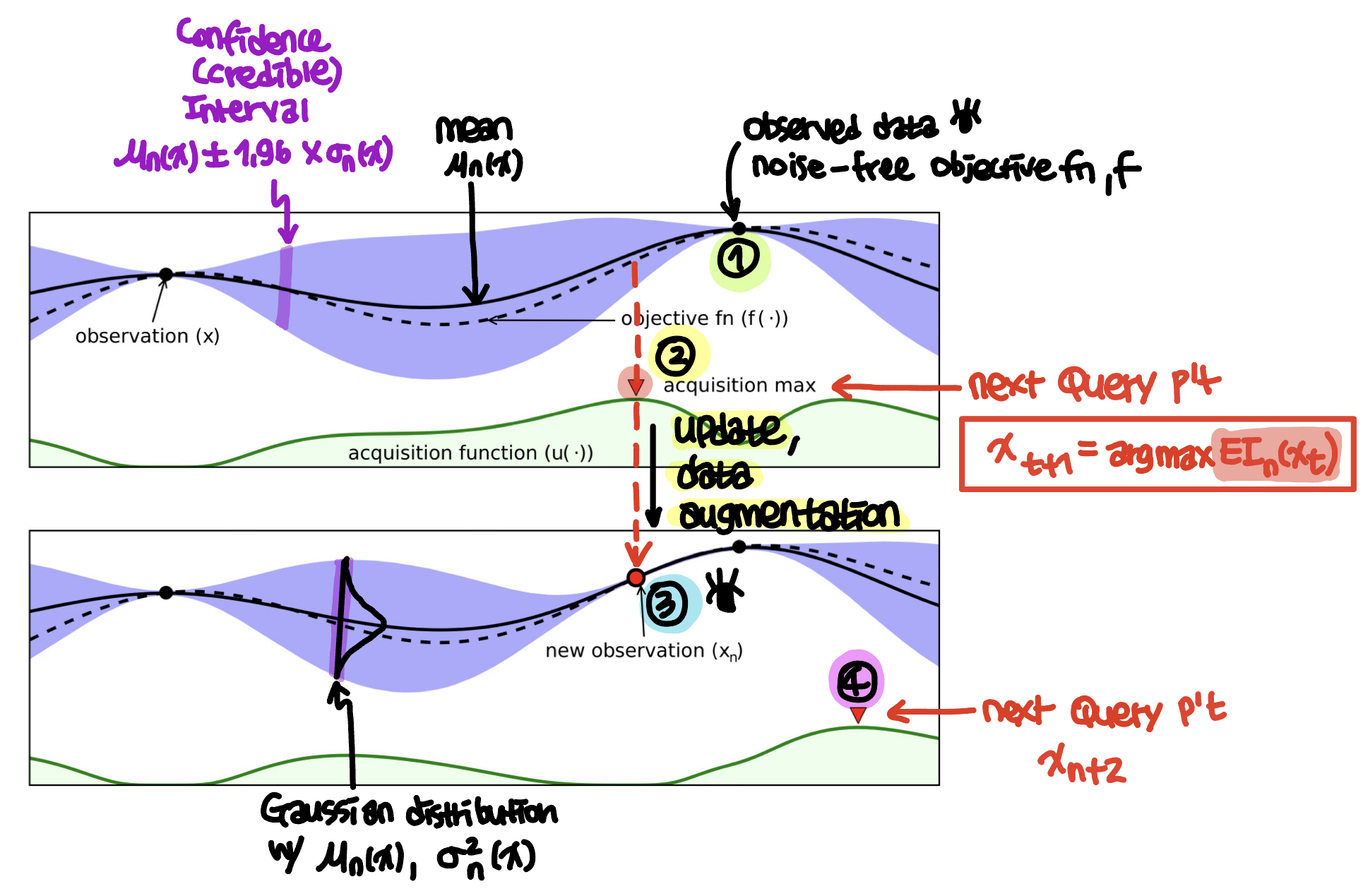
Fig. Schematic of BO w/ comments by SS
GPR을 통해 mean, 𝝁과 variance, 𝝈^2를 갖는 Bayesian posterial probability distribution을 구하게 되는데, 그림에서 solid line은 mean 값을 나타내고, 보라색 shaded region은 Bayesian credible interval로

이다. 이는 frequentist statistics에서 confidence interval 같은 역할을 하며 posterial probability에 따라 확률이 95% (이는 2𝝈에 해당함)인 f(x)를 포함한다 [15]. 이 shaded region은 우리가 알고 있는 observed data (검은색 점)에서는 0값을 갖지만, 우리가 모르는 값들의 경우 값을 갖는다. 그리고 observed data에서 멀어질수록 그 값이 커진다.
그리고 그림의 아래 green shaded region은 acquisition function 값을 의미하는데, 이 것이 maximum value를 갖는 데이터 포인트가 next query p’t가 된다. 자세한 내용은 아래 ☻ Acquisition function에서 자세히 다루도록 하자.
☻ Objective function, f
자, 이제 objective function이다.
이 objective function은 목적함수로 베이지안 최적화에서는 이 함수를 최적화하는 것이 중요하다. 이러한 objective function의 특징으로는 다음과 같다 [1,13].
◦ Continuous
◦ Expensive to evaluate
◦ Black-box (unknown struction)
◦ derivative free : prevents the application of first- and second-order methods
◦ noise-free : be observed w/o noise
◦ nonlinear
◦ non-convex function
◦ global optimum
그래서 간단하게 한문장으로 정리하자면,
We summarize these problem characteristics by saying that BayesOpt is designed for black-box derivative-free global optimization [1].
여기서 objective function을 black-box라고 하는 이유는 어떠한 형태인지, derivative되는지 등 아무것도 모르는 black-box의 상태로 존재하며, input으로 x가 들어가서 output으로 f(x)가 나온다는 것만 알고 있기 때문이다.(아래 schematic은 제가 작성한 것 입니다.).
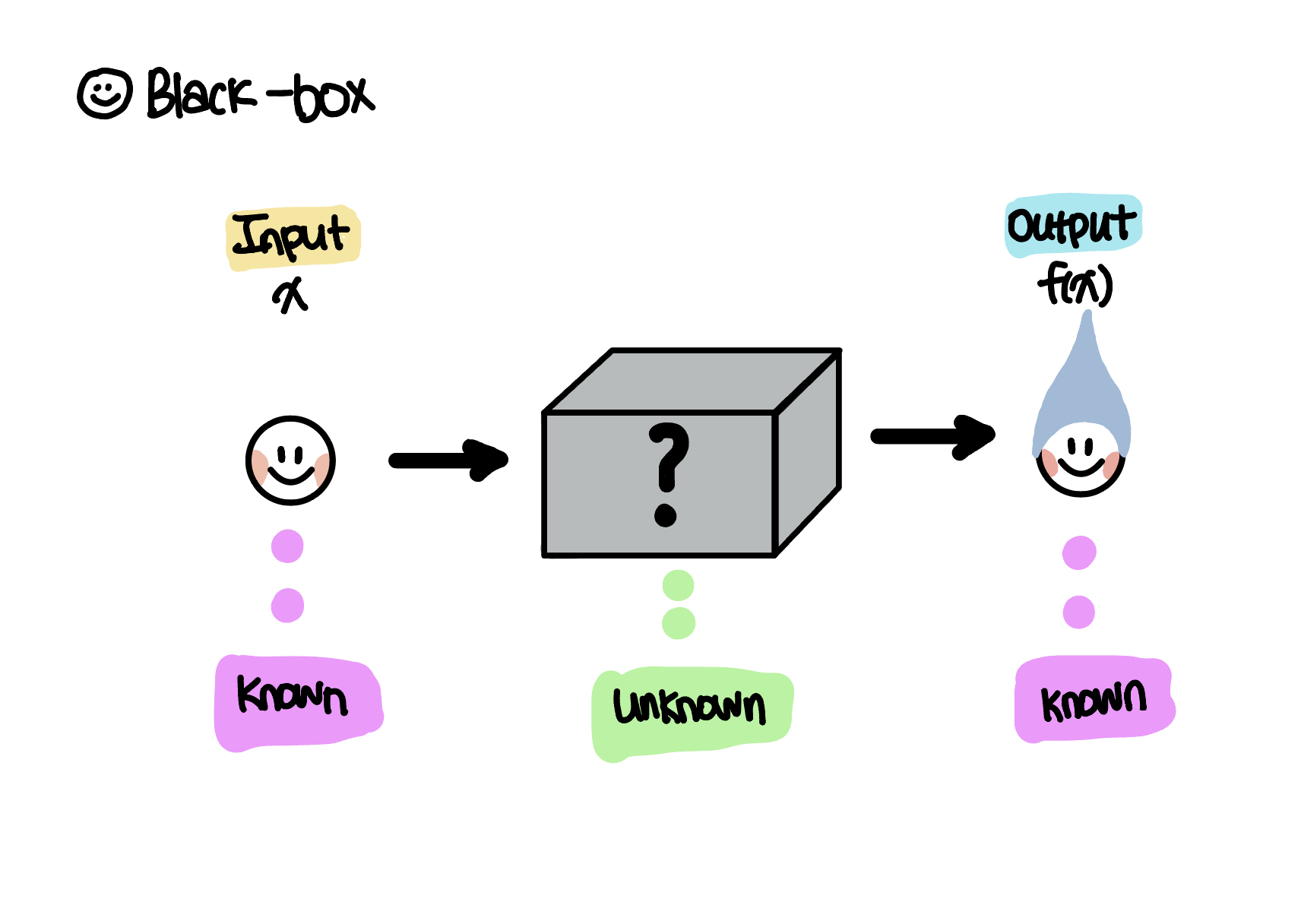
이러한 objective function을 구하는 것이 우리의 quest이며, 이때 사용되는 것이 이제 살펴볼 surrogate model이다.
☻ Surrogate model
surrogate model은 blackbox function을 위한 statistic/probabilistic 모델링으로, 미지의 objective function을 확률적으로 추정하는 모델이라고 볼 수 있다.
surrogate의 사전적 의미를 확인해보면 대리의, 대용의라는 의미를 포함하고 있다 [16].
◦ surrogate
: someone or something that replaces or is used instead of someone or something else; a substitute for another
A surrogate model is an engineering method used when an outcome of interest cannot be easily measured or computed, so a model of the outcome is used instead. Most engineering design problems require experiments and/or simulations to evaluate design objective and constraint functions as a function of design variables [17].
ML관점에서 surrogate model을 확인하면 아래와 같다 [18].
복잡하고 설명하기 힘든 모형(블랙박스 모형)을 단순하고 설명하기 쉬운 모형(대리 모형)으로 대신 설명하는 방법을 말한다. 선형회귀 모형, 로지스틱 회귀모형, 트리모형 등의 설명 가능한 모형을 대리 모형으로 사용할 수 있다. 대리 모형은 학습시키는 방식에 따라 크게 두 가지 방향으로 분류해 볼 수 있다. train 데이터의 전부 또는 일부를 대리 모형으로 다시 학습하여 사용하는 방법을 전역적 대리 모형(global surrogate model)이라 하고, 특정 데이터 포인트 근방에서 샘플링된 데이터를 활용하여 대리 모형을 학습하여 사용하는 방법을 국소적 대리 모형(local surrogate model)이라고 한다.
따라서 black-box인 objective function을 설명하기위해 고려한 것이 surrogate model (대리모형)이라고 볼 수 있고, 우리는 Bayes Theorem을 기반으로 하고 있는 GPR을 사용하게 됨에 따라 본 최적화 방법이 Bayesian Optimization이 되는 것이다.
뭐.. 조금은 그럭저럭 이해가 되는 같다.

자, 다시 논문으로 돌아가서 확인해보자.
우선, k개의 데이터 포인트가 있고

그에 대응하는 함수값들이 vector의 형태로 다음과 같이 존재 할 때,

i 번째 데이터 포인트에서 mean function (평균 함수)과 covariance function (or kernel) (두 입력 간의 유사도를 반영) 은
 이다.
이다.
여기서 normal distiribution의 형태를 갖는 Prior distribution은 아래와 같다.

여기서 1:k는 1번째부터 k번째 값을 포함하는 벡터를 의미한다

이제, n+1번째 새로운 데이터를 k라고 놓고, 이때 f(x)에 대한 conditional distribution (posterior probability)를 구하면 아래와 같다.



즉, Gaussian Process Regression (GPR)을 이용해서 mean과 covariance를 구하고, 이 값들을 aquisition function에 업데이트 시켜준다. 이때, covariance는 기존에 측정한 다른값들과의 유사도를 바탕으로 하고, 두 데이터 값이 가까우면 큰 값을 멀면 작은 값을 반환한다 [1,19].
☻ Acquisition function
Acquisition function은 다음 step에서 탐색할 입력값 후보 추천하는 함수로 surrogate model에서 준 mean과 variance 값을 이용하고 있다. 이때, 중요한 역할은 exploition과 exploration의 balance를 잘 맞추는 것이 중요하다.

They all trade-off exploration and exploitation so as to minimize the number of function queries [13].
언급하였듯이 exploitation 과 exploration은 trade off관계로 exploitation은 우리가 알고 있는 영역 그리고 exploration은 우리가 잘 모르는 영역 을 의미한다 [20].
Exploration ensures the algorithm to reach different promising regions of the search space, whereas exploitation ensures the searching of optimal solutions within the given region. The fine tuning of these components is required to achieve the optimal solution for a given problem. It is difficult to balance between these components due to stochastic nature of optimization problem. This fact motivates us to develop a novel metaheuristic algorithm for solving real-life engineering design problem. The performance of one optimizer to solve the set of problem does not guarantee to solve all optimization problems with different natures.
우리가 알고 있는 정보로 exploitation과 exploration에 대해서 이해해보면 다음과 같다[21,22].
◦ Exploitation : posterial mean 이 높은 영역
◦ Exploration : posterial variance가 높은 영역
Choose the next x where the posterior mean is hight (exploitation) and the posterior variance is high (exploration).
즉, 두개의 balance를 잘 맞춰주는 것이 Acquisition function 의 역할이라고 볼 수 있다.
Comparing two points x1 and x2: if their means are the same, then BO will pick the one that has larger σ2(x). This is called exploration.Comparing two points x1 and x2: if their variances are the same, then BO will pick the one that has larger μ(x). This is called exploitation [22].
이러한 Acquisitoin functions으로는 아래와 같이 다양한 방법이 있다 [1].
◦ Probability of Improvement (PI)
◦ Expected Improvement (EI)
◦ Bayesian expeced losses
◦ Upper confindence bouncds (UCB)
◦ Thompson smapling
◦ GP Upper Con dence Bound (GP-UCB)
◦ Entropy search
◦ Knowledge gradient
여기서 우리가 고려한 것은 Expected Improvement (EI)이고, 이러한 배경으로는 사용하기 편하고 성능이 좋기 때문이다 [1,13].
The expected improvement acquisition function is derived by a thought experiment.
EI를 정리하면,

f* 는 현재까지 관측한 함수의 최대값으로 아래와 같이 표현 가능하다.

따라서, 다음 step의 query p’t는

로 EI값이 최대인 점을 반환하게 된다.
자세한 설명에 대해서는 많이 생략한 부분이 있지만, 그래도 Bo (BayesOpt)에 대해서 좀 이해가 되는 것 같다. 좀 더 궁금하다면 논문들을 읽어 볼 것을 추천한다.
아무튼, Bayes theorem 과 Optimization 의 만남이란 환상적이구나~~

글을 작성한다는 것은 내가 배운 것을 공유한다는 관점에서는 재밌고 뿌듯함을 느낀다. 하지만 한편으로는 무척이나 조심스럽고 큰 책임감을 느낀다.
모든 일에는 책임감이 따르기 마련이니 수정할 부분이 있다면 추후에도 계속 업데이트할 예정이다.
공부해야 할 것도 많고, 배우고 싶은 것들도 많고, 갈 길도 좀 멀지만 그래도 조금씩 그리고 꾸준히 나아가보자 한다.

☻ Reference
- Paper : A Tutorial on Bayesian Optimization
- wikipedia : Bayesian Optimization
- Machine Learning Mastery : How to Implement Bayesian Optimization from Scratch in Python
- wikipedia : 수학적 최적화
- wikipedia : Optimization problem
- Book (개인 소장): Mathematics for Machine Learning by Book by A. Aldo Faisal, Cheng Soon Ong, and Marc Peter Deisenroth
- wikipedia : Global optimization
- Machine Learning Mastery : Local Optimization versus Global Optimization
- 네이버 국어/영어사전
- 7 Hyperparameter Optimization Techniques Every Data Scientist Should Know
- Parameters and Hyperparameters in Machine Learning and Deep Learning
- Definition of hyper-
- wikipedia : Bayesian Optimization
- Paper :Taking the Human Out of the Loop: A Review of Bayesian Optimization (2016)
- wikipedia “ 68-95-99.7 rule
- cambridge dictionary : surrogate
- wikipedia : surrogate model
- 대리모형
- 논문리뷰:베이지안 최적화 (Bayesian Optimization)
- What is Exploitation and Exploration in Optimization Algorithms?
- Epxloration and Exploitation
- How does Bayesian Optimization balance exploration with exploitation?
Code : 베이지안 최적화
☻ image sources
모두의 연구소에서 진행하는 “함께 콘텐츠를 제작하는 콘텐츠 크리에이터 모임”인 COCRE(코크리) 의 2기 회원으로 제작한 글입니다